Frame Size and Wireshark
Frame Size and Wireshark
This blog is a write up of what was discussed at our first AMA session:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TM70jXEsFsk
In Wireshark, when you look at the frame sizes, by viewing the “Length” field, it reports a number to you. This is the frame length. You can view this by looking under the Frame section of Wireshark.
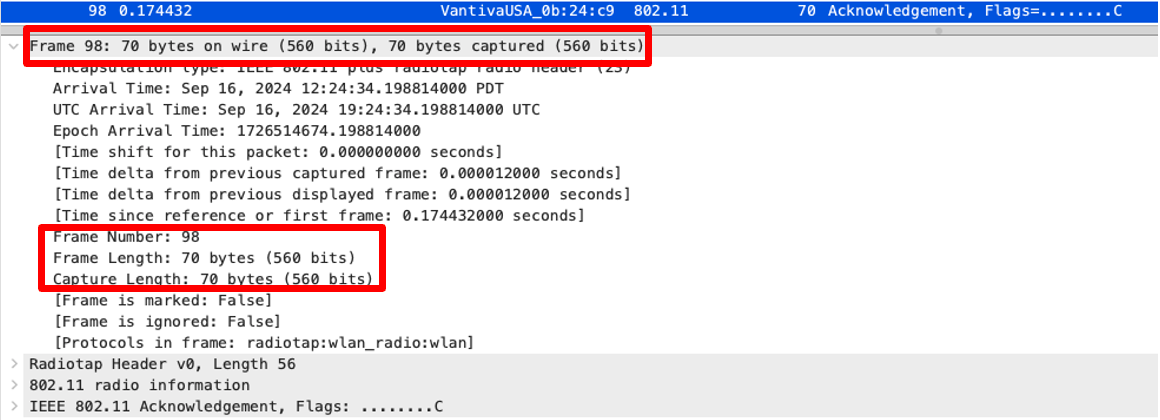
You can of course add this as a column in Wireshark.
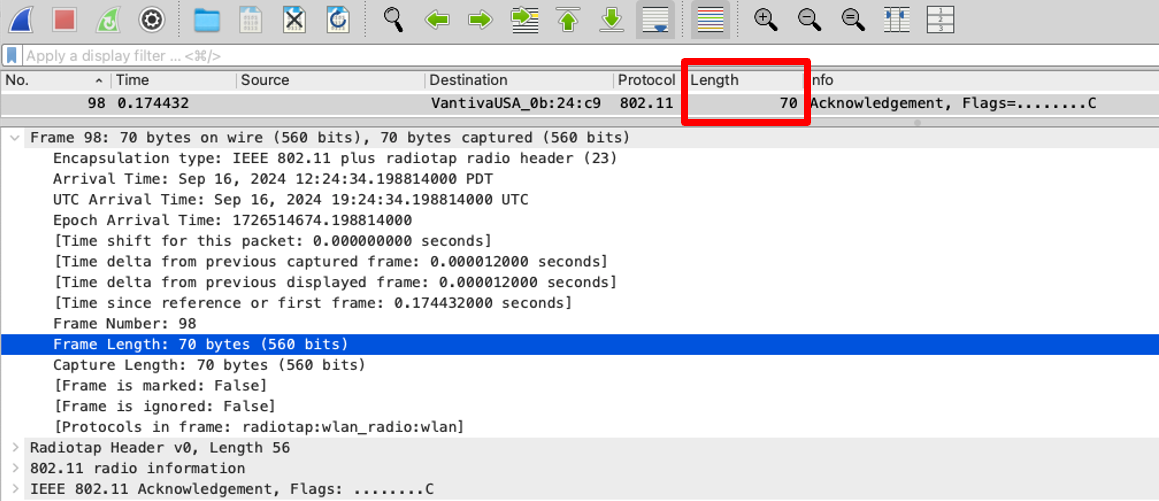
Well, it’s lying to you. Everyone knows that ACKs are 14 Bytes, not 70!
What? Why? How?...
Well, this is actually quite simple. Wireshark is reporting the size of the frame, INCLUDING the radiotap header.
The radiotap header is added by the capturing device, and it gives you all sort of information about the frame when it was captured.
Different capturing devices, and software, do this differently. While there are standard formats for storing this information, different applications will do this differently. Also, it depends on which protocol you are capturing. So, essentially, different protocols have different frame sizes based on information that different applications store!!!
So, a capture made with one capturing device, may use different frame sizes than a capture made on a different tool. Also, these numbers depend on what protocol is being captured 802.11n, ac, ax, or be, etc.
This number is essentially the frame size in the pcap file, including the radiotap header.
Can you turn this off, or adjust it?
Simple answer: NO!
However, there is a little trick you can do, and that is to display the radiotap header size next to the length.
Simply add the Radiotap Header > Header Length as a column, and you can see what you need to see!
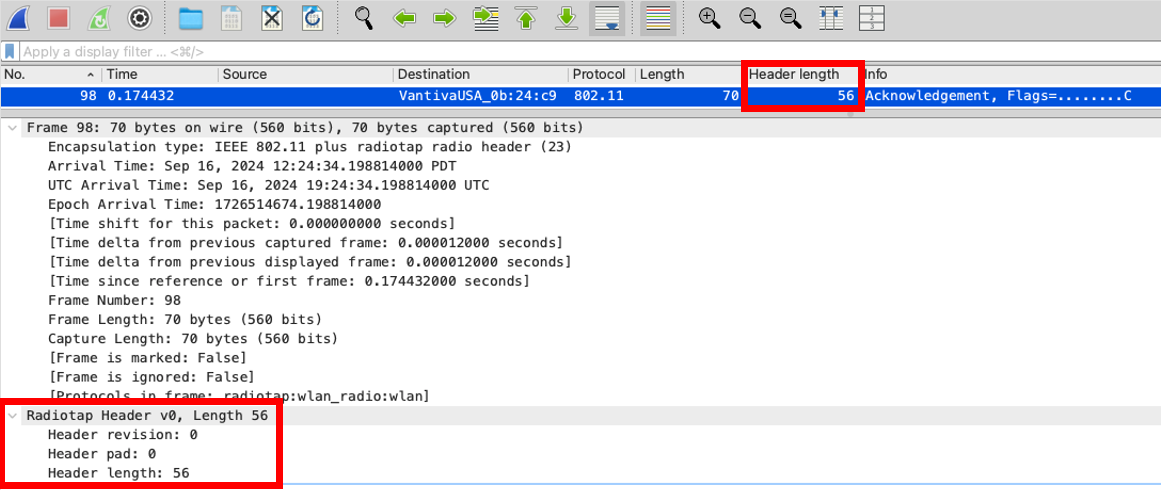
Then you can do a quick math sum, and work out the real size of the frame!
70-56 = 14 just like it should be!
See you next time!
===
#General #WiFi #WirelessFrames #Wireshark
===
About NC-Expert
NC-Expert is a privately-held California corporation and is well established within the Wireless, Security, and Collaboration industry certification training, courseware development, and consulting markets.
Led by its Founder and CEO, Rie Vainstein, NC-Expert has won numerous private contracts with Fortune level companies around the world. These customers have depended on NC-Expert to train, advise, and mentor their staff.
So remember, if you are looking for the best IT training just call us at (855) 941-2121 or contact us
NC-Expert Blog





